Young's Modulus Calculator
The SkyCiv Young's Modulus Calculator allows you to estimate Young's Modulus (also commonly known as Elastic Modulus or Tensile Modulus) based on Stress/Strain data. Young's Modulus is a vital property for engineers that is used to determine the stiffness or rigidity of a material. The calculator contains two modes for calculating Young's Modulus. The first mode calculates stress and strain values from the force, area, and initial and final length properties. The second mode estimates Young's Modulus using Linear Regression from a Stress-Strain Curve. To get started and learn how to calculate Young's Modulus enter your properties below and click run.
About this Young’s Modulus Calculator
What is Young’s Modulus?
Young’s Modulus, commonly referred to as Elastic Modulus or Tensile Modulus, is a critical material property used to characterise the stiffness or rigidity of a material. It represents the ratio between stress and strain within a material which experiences either tensile or compressive forces.
Why is Young’s Modulus Important?
The Young’s Modulus value is a vital material property which measures a material's stiffness and ability to resist deformation under tensile or compressive forces. This measurement can be used to help predict how materials behave upon applied loads and make optimised selections on material for desired applications.
How is Young’s Modulus Calculated?
Two distinct methods which can be used to calculate Young’s Modulus include:
- Stress / Strain Data
- Stress-Strain Curve
The Stress / Strain Data is determined by factors which include Force (F) and Area (A) for Stress (σ) and Final Length (Lf) and Initial Length (Li) for Strain (ϵ). The formula to calculate stress and strain using the data is as follows:

Once Stress / Strain Data have been used to calculate Stress (σ) and Strain (ϵ) values, they can be used to calculate the Young’s Modulus (E) in the following formula:
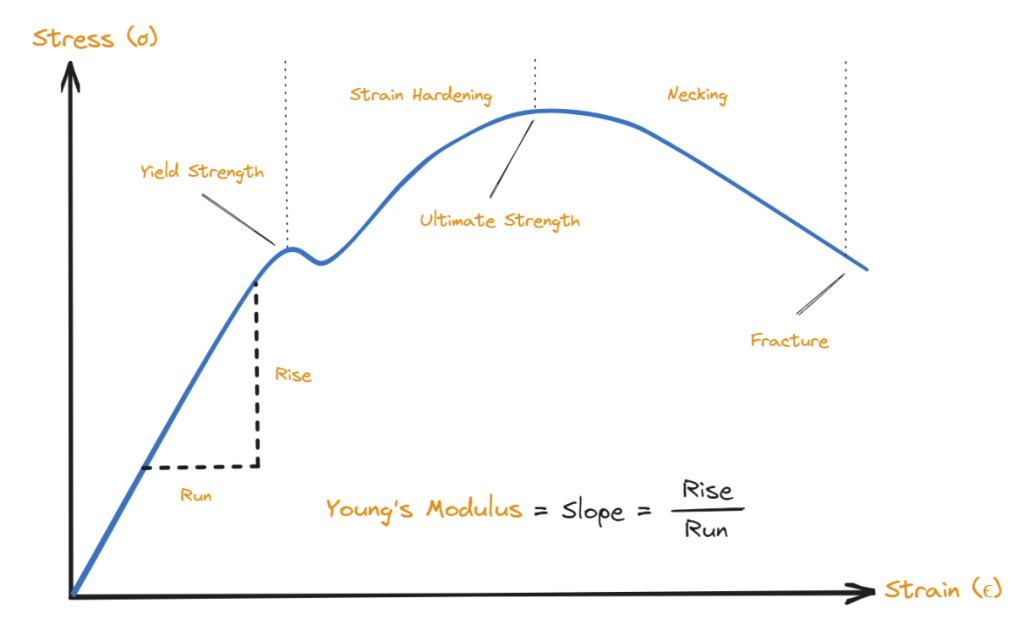
How to calculate Young’s Modulus from a Stress-Strain Curve?
Using a minimum of three stress-strain coordinates, these points can be plotted on the Stress-Strain Chart, and a linear regression line can be formed. This option is available in the Young’s Modulus Calculator above. From this linear regression line, the slope can be determined, which also represents Young’s Modulus (E) value.
Young's Modulus Calculator FAQs
What options for calculation are available in the Young's Modulus Calculator?
The Young's Modulus Calculator allows you to calculate Young's Modulus via either stress and strain data or by alternatively calculating this property from a stress-strain curve.
What does a high Young's Modulus mean?
A high Young's Modulus value indicates that the material is stiff and rigid, which means that it is less elastic and more resistant to deformation under an applied load. Alternatively, a low Young's Modulus indicates that a material will deform easily under an applied force and has lower stiffness.
Does Young's Modulus change with temperature?
In most cases, as temperature increases Young's Modulus tends to decrease depending on the thermal properties of the material. In some rare cases, certain materials may experience an increase in Young's Modulus as temperature increases.